D-Phenylalanine
-
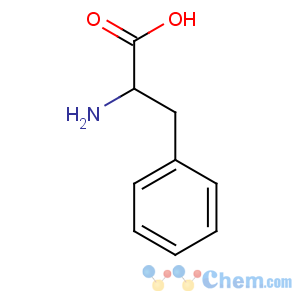
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Product Name:D-Phenylalanine
Synonyms: D-beta-Phenyl-alpha-aminopropionic acid;d-alpha-aminohydrocinnamic acid;D-ALPHA-AMINO-BETA-PHENYL-PROPIONIC ACID;D-2-AMINO-3-
PHENYLPROPANOIC ACID;D(+)-PHENYLALANINE;D-PHENYLALANINE;d-phe;H-D-PHE-OH
CAS: 673-06-3
MF:C9H11NO2
MW: 165.19
EINECS: 211-603-5
Chemical Properties: White crystalline powder
Product Categories: Benzene derivatives; Amino ACIDS SERIES;Aromatic Propionic Acids; Phenylalanine [Phe, F]; Amino Acids and Derivatives; alpha-Amino Acids; Amino Acids; Biochemistry;Amino Acids; amino acid; chemicals; organic acids; pharmaceutical intermediate; phenlalnine; Nateglinid
mp: 273-276 °C(lit.)
alpha: 33.5 o (c=2, H2O)
refractive index : 34 ° (C=2, H2O)
storage temp: Store at RT.
Water Solubility: 27 g/L (20 oC)
Merck: 14,7271
BRN : 2804068
Stability: Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, acids, bases.
Use:D-Phenylalanine, the stereoisomer of L-Phenylalanine (P319415) has been used in the synthesis of Schaeffer acid analogues as important structures in tuberculostatic design. They exhibit the ability to inhibit Mycobacterium tuberculosis type II dehydroquinase.

- D-Phenylalanine




