L-Arginine
-
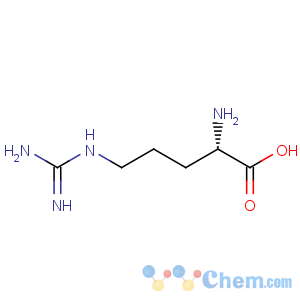
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
L-Arginine
Synonyms: ARG;L-ARG;H-ARG-OH; L(+)-ARGININE;L-ARGININE;L-ARGININE BASE;L-ARG;L-2-AMINO-5-GUANIDINOVALERIC ACID;ARG;ARGININE, L-;FEMA 3819
Product Categories: pharmacetical;chiral;Arginine [Arg, R];Amino Acids;Amino Acids and Derivatives;for Resolution of Acids;Optical Resolution;alpha-Amino Acids;Biochemistry;Synthetic Organic Chemistry;L-Amino Acids;Amino Acids;Nitric Oxide;amino
CAS: 74-79-3
MF: C6H14N4O2
MW: 174.2
mp 222 °C (dec.)(lit.)
solubility H2O: 100 mg/mL
Appearance: white crystal or white powder, bitter, melt in water
Functions: Arginine is a part of ornithine, which has tremendous effect of physiometry. L-arginine has been used for erectile dysfunction. Like the drug Weilinafil citrate (Viagra), L-arginine is thought to enhance the action of nitric oxide, which relaxes muscles surrounding blood vessels supplying the penis. As a result, blood vessels in the penis dilate, increasing blood flow, which helps maintain an erection. The difference in how they work is that Viagra blocks an enzyme called PDE5 which destroys nitric oxide and L-argentine is used to make nitric oxide.

- L-Arginine




