Tranexamic Acid
-
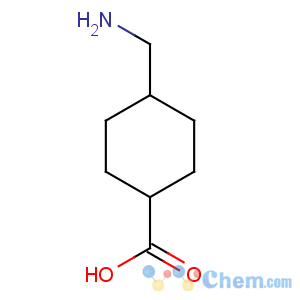
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
CAS 1197-18-8 Tranexamic Acid
Product Name: Tranexamic Acid,amstat,tranexa,transamic acid
Synonyms:trans-4-(Aminomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic acid;trans-4-aminomethylcyclohexane-1-carboxylate;amcha;exacyl,tranexamicacid
CAS No.: 1197-18-8
EINECS No.: 214-818-2
Molecular Formula: C8H15NO2
Molecular Weight: 157.21
Melting point: >300 °C(lit.)
Appearance: white powder
Application: Mainly used for Whitening freckle,Hemostasis
Tranexamic acid is a synthetic analog of the amino acid lysine. It is used to treat or prevent excessive blood loss during surgery and in various medical conditions or disorders (helping hemostasis). It is an antifibrinolytic that competitively inhibits the activation of plasminogen to plasmin, by binding to specific sites of both plasminogen and plasmin, a molecule responsible for the degradation of fibrin, a protein that forms the framework of blood clots. Tranexamic acid has roughly eight times the antifibrinolytic activity of an older analogue, ε-aminocaproic acid.
Tranexamic acid is frequently used in surgeries with high risk of blood loss such as heart, liver, vascular and large orthopedic procedures. Its oral form is now being evaluated for use in outpatient conditions involving heavy bleeding.

- Tranexamic Acid




