Maltol
-
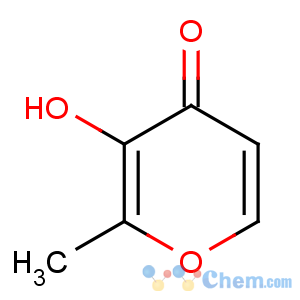
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Product name:Maltol
Synonyms:3-Hydroxy-2-methyl-4-pyrone;3-Hydroxy-2-methyl-4H-pyran-4-one
CAS:118-71-8
EINECS:204-271-8
MF:C6H6O3
MW:126.11
Melting point:160-164oC
Boiling point:170oC(10MMHG)
Water solubility:1.2G/100ML(25oC)
Appearence:white crystalline powder
Assay:99%
standard:FCC IV
Usage:
A fragrance molecule used in flavor enhancers and fragrances.
General Description:White crystalline powder with a fragrant caramel-butterscotch odor. pH (5% aqueous solution) 5.3.
Air & Water Reactions:May be sensitive to prolonged exposure to light and air. Somewhat soluble in water at room temperature. Freely soluble in hot water [Merck]. Slightly soluble in cold water.
Description:
Maltol is a naturally occurring organic compound that is used primarily as a flavor enhancer. It is found in the bark of larch tree, in pine needles, and in roasted malt (from which it gets its name). It is a white crystalline powder that is soluble in hot water, chloroform, and other polar solvents. Because it has the odor of cotton candy and caramel, maltol is used to impart a sweet aroma to fragrances. Maltol's sweetness adds to the odor of freshly baked bread, and is used as a flavor enhancer (INS Number 636) in breads and cakes. It is not registered as a food additive in the EU and thus has no E-number.Instead, maltol is registered as a flavor component in the EU.
Maltol, like related 3-hydroxy-4-pyrones such as kojic acid, binds to hard metal centers such as Fe3+, Ga3+, Al3+, and VO2+. Related to this property, maltol has been reported to greatly increase aluminum uptake in the body and to increase the oral bioavailability of gallium and iron.

- Maltol




