Salirasib
-
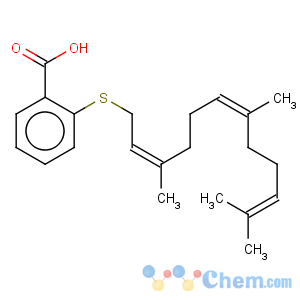
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Salirasib is a salicylic acid derivative with potential antineoplastic activity. Salirasib dislodges all Ras isoforms from their membrane-anchoring sites, thereby preventing activation of RAS signaling cascades that mediated cell proliferation, differentiation, and senescence. RAS signaling is believed to be abnormally activated in one-third of human cancers, including cancers of the pancreas, colon, lung and breast. Salirasib binds to a cell membrane anchor protein thereby selectively blocking a cascade of biochemical signals known as the Ras signaling pathway. The Ras pathway plays an important role in tumor growth and is believed to be abnormally activated in one-third of human cancers, including cancers of the pancreas, colon, lung and breast. Up to 90% of human pancreatic cancers are driven by aberrant oncogenic Ras signaling.

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure
