trans-Cinnamic acid
-
- Product Nametrans-Cinnamic acid
- CAS No.140-10-3
- Purity99%
- Min Quantity1000Kilograms
- Price1~10

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail
-
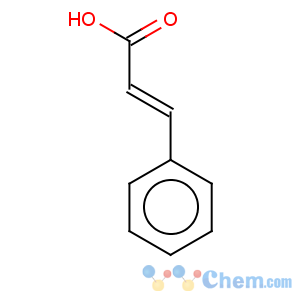 Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Cinnamic acid is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CHCHCO2H. It is a white crystalline compound that is slightly soluble in water, and freely soluble in many organic solvents. Classified as an unsaturated carboxylic acid, it occurs naturally in a number of plants. It exists as both a cis and a trans isomer, although the latter is more common.Cinnamic acid is used in flavors, synthetic indigo, and certain pharmaceuticals. A major use is in the manufacturing of the methyl, ethyl, and benzyl esters for the perfume industry.Cinnamic acid is a precursor to the sweetener aspartame via enzyme-catalysed amination to phenylalanine.Cinnamic acid can dimerize in non-polar solvents resulting in different linear free energy relationships