Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate
-
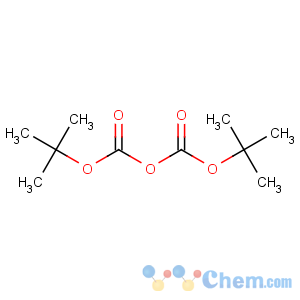
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is a reagent widely used in organic synthesis.[1] Since this compound can be regarded formally as the acid anhydride derived from a tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) group, it is commonly referred to as "Boc anhydride." This pyrocarbonate reacts with amines to give N-tert-butoxycarbonyl or so-called Boc derivatives. These carbamate derivatives do not behave as amines, which allows certain subsequent transformations to occur that would be incompatible with the amine functional group. The Boc group can later be removed from the amine using moderately strong acids (e.g., trifluoroacetic acid). Thus, Boc serves as a protective group, for instance in solid phase peptide synthesis. Boc-protected amines are unreactive to most bases and nucleophiles, allowing for the use of the fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl group (Fmoc) as an orthogonal protecting group.

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure
