Chitin
-
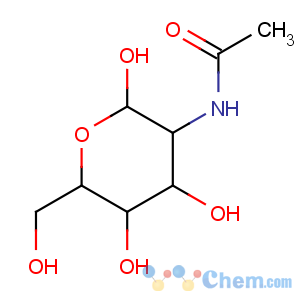
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Product name:Chitin
Synonyms:beta-(1,4)-2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucose
CAS:1398-61-4
EINECS:215-744-3
MF:(C8H13NO5)n
MW:(203.19)n
Water solubility:insoluble
Appearence:Amorphous white translucent material
Uses:
(1)Agriculture:
Most recent studies point out that chitin is a good inducer of defense mechanisms in plants.It has also been assessed as a fertilizer that can improve overall crop yields.The EPA regulates chitin for agricultural use within the USA.Chitosan is prepared from chitin by deacetylation.
(2)Industrial:
Chitin is used in industry in many processes. Examples of the potential uses of chemically modified chitin in food processing include the formation edible films and as an additive to thicken and stabilize foods and pharmaceuticals. It also acts as a binder in dyes, fabrics, and adhesives.Industrial separation membranes and ion-exchange media can be made from chitin. Processes to size and strengthen paper employ chitin and chitosan.Researchers have developed a method for using chitosan as a reproducible form of biodegradable plastic and as a promising substrate for engineering human tissues by use of three-dimensional bioprinting.
(3)Medicine:
Chitin's flexibility and strength make it favorable as surgical thread. Its biodegradibility means it wears away with time as the wound heals. Moreover, chitin has been reported to have some unusual properties that accelerate healing of wounds in humans. Occupations associated with high environmental chitin levels, such as shellfish processors, are prone to high incidences of asthma. Recent studies have suggested that chitin may play a role in a possible pathway in human allergic disease. To be specific, mice treated with chitin develop an allergic response, characterized by a build-up of interleukin-4-expressing innate immune cells. In these treated mice, additional treatment with a chitinase enzyme abolishes the response.
(4)Biomedical research:
Chitin may be employed for affinity purification of recombinant protein. A chitin binding moiety is genetically fused to a protein of interest and then connected to beads coated with chitin. The immobilized protein is purified and released from the beads by cleaving off the chitin binding moiety.

- Chitin




