BHT
-
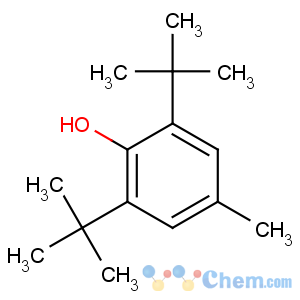
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Product name:BHT
Synonyms:BHT;Butylated hydroxytoluene;DBPC;2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol
CAS:128-37-0
EINECS:204-881-4
MF:C15H24O
MW:220.35
Melting point:69-71oC
Boiling point:265oC
Flashing point:127oC
Density:1.048
Water solubility:insoluble
Appearence:white or light yellow crystalline powder
Assay:99.7%
Applications:
(1)Food additive
BHT is primarily used as a food additive that exploits its antioxidant properties. In the United States, it is classified as generally recognized as safe (GRAS).It is approved for use in European Union under E321 and in the U.S. by the Food and Drug Administration via regulation: For example, 21 CFR allows BHT up to 0.0033% by weight in "enriched rice", while 9 CFR allows up to 0.01% in poultry "by fat content". Meanwhile, it is forbidden to apply as food additive in Japan (since 1958), Romania, Sweden, and Australia. Nonetheless, some food companies have voluntarily eliminated this additive from their products, and since the 1970s, it has been steadily replaced with BHA.
(2)Antioxidant
BHT is also used as an antioxidant additive in such diverse products as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, rubber, electrical transformer oil (at 0.35%),and embalming fluid. In the petroleum industry, where BHT is known as the fuel additive AO-29, it also finds uses in hydraulic fluids, turbine and gear oils, and jet fuels,[9] among other applications. BHT is also used to prevent peroxide formation in diethyl ether and other laboratory chemicals.
Some additive products contain BHT as their primary ingredient, while others contain the chemical merely as a component of their formulation, sometimes alongside butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA).

- BHT




