Paracetamol
-
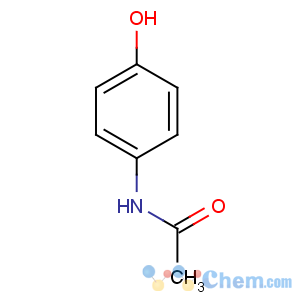
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
CAS 103-90-2 Paracetamol
Pharmacetical Raw Materials Paracetamol Cas 103-90-2 for Anti inflammatory
Product Name: Paracetamol
Assay: 99%
CAS No.: 103-90-2
EINECS No.: 203-157-5
Molecular Formula: C8H9NO2
Molecular Weight: 151.16
Melting point: 168-172 ° C(lit. )
Appearance: White crystalline powder
Packing: 25KG/Drum
Application: Antipyretic Analgesics
Usage:used as analgesic-antipyretic pharmaceutical material
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen or APAP, chemically named N-acetyl-p-aminophenol, is a widely used over-the-counter analgesic (pain reliever) and antipyretic (fever reducer). Acetaminophen is the name adopted for this pharmacologic agent in the U. S. (USAN) and Japan; Paracetamol is approved in a variety of international venues (INN, AAN, BAN, etc. ). Common trade names in English-speaking markets are Tylenol and Panadol.
Paracetamol is classified as a mild analgesic. It is commonly used for the relief of headaches and other minor aches and pains and is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu remedies. In combination with opioid analgesics, paracetamol can also be used in the management of more severe pain such as post-surgical pain and providing palliative care in advanced cancer patients. Though paracetamol is used to treat inflammatory pain, it is not generally classified as an NSAID because it exhibits only weak anti-inflammatory activity.
Fever
Paracetamol is approved for reducing fever in people of all ages. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that paracetamol be used to treat fever in children only if their temperature is greater than 38.5 ° C (101.3 ° F). The efficacy of paracetamol by itself in children with fevers has been questioned and a meta-analysis showed that it is less effective than ibuprofen.
Pain
Paracetamol is used for the relief of pains associated with many parts of the body. It has analgesic properties comparable to those of aspirin, while its anti-inflammatory effects are weaker. It is better tolerated than aspirin in patients in whom excessive gastric acid secretion or prolongation of bleeding time may be a concern. Available without a prescription since 1959, it has since become a common household drug.
Paracetamol has relatively little anti-inflammatory activity, unlike other common analgesics such as the NSAIDs aspirin and ibuprofen, but ibuprofen and paracetamol have similar effects in the treatment of headache. Paracetamol can relieve pain in mild arthritis, but has no effect on the underlying inflammation, redness, and swelling of the joint.

- Paracetamol




