L-Glutamine
-
- Product NameL-Glutamine
- CAS No.56-85-9
- Purity
- Min Quantity
- Price~

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail
-
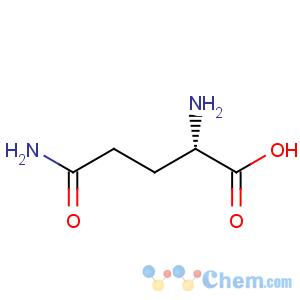 Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure

- L-Glutamine
Detailed Description
Name: L-GlutamineSynonyms: 2-Aminoglutaramic acid; Levoglutamide; L(+)-Glutamic acid-5-amide
Molecular Formula: C5H10N2O3
Molecular Weight: 146.14
CAS Registry Number: 56-85-9
Appearance: white crystal powder
Melting Point: 185 oC
Assay: 98%min
Function and Usage:
1. L-Glutamine is the most prevalent amino acid in the bloodstream.
2. L-Glutamine is involved in more metabolic processes than any other amino acid.
3. L-Glutamine is converted to glucose when more glucose is required by the body as an energy source.
4. L-Glutamine also plays a part in maintaining proper blood glucose levels and the right pH range.
5. L-Glutamine serves as a source of fuel for cells lining the intestines. Without it, these cells waste away.
6. L-Glutamine is also used by white blood cells and is important for immune function.
Packaging: 25kg/drum or according to customer's require