Nandrolone
-
- Product NameNandrolone
- CAS No.434-22-0
- Purity
- Min Quantity
- Price~

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail
-
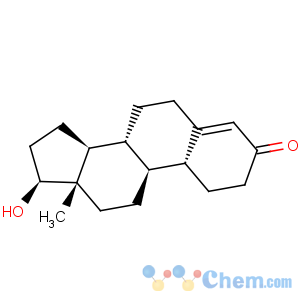 Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Data of Nandrolone Base Powder:Nandrolone No ester Alias: Norandrostenolone
Nandrolone No ester CAS ID: 434-22-0
Nandrolone No ester M.F.: C18H26O2
Nandrolone No ester M.W.: 274.4
Nandrolone No ester Purity: 99.29% by HPLC
Nandrolone No ester Melting point: 121.3~123.6°C
Nandrolone No ester Appearance: White Powder or Almost White Crystalline Powder.
Genaral Information of Nandrolone No ester Powder:
Nandrolone is relatively safe in terms of a user's lipid profile and cholesterol. In some studies it has even been shown to actually improve HDL cholesterol levels. A major increase in a user's blood pressure or their liver toxicity should not be noticed with this compound either. Both are relatively mild in these respects.
Nandrolone is a modification of testosterone (carbon atom removed from the 19th position) With an Anabolic/Androgenic ratio: 125:37, meaning it is highly anabolic (muscle building) and moderately androgenic (male characteristics). Due to nandrolones chemical structure it only aromatizes (converts to estrogen) slightly, at about 20% the rate of testosterone when it interacts with the aromatase enzyme. Ergo, estrogenic effects are not a major concern with its use.
Of note, however, is that nandrolone is a progestin with a binding affinity of 20% to the progesterone receptor, so side effects are still possible, though rare. The development of breast tissue in males (gynecomastia) has been reported in some steroid.com users. One of the most popular anabolic steroid used in bodybuilding cycles, nandrolone is also (medically) used to treat severe debility or disease states and refractory anemias. It promotes tissue building processes, reverses catabolism (muscle destruction) and stimulates erythropoiesis (red blood cell production). This makes it a very useful drug to treat wasting disorders such as advanced H.I.V. , and also, makes it highly sought after by bodybuilders and athletes.