L(-)-Carnitine
-
- Product NameL(-)-Carnitine
- CAS No.541-15-1
- Purity99%
- Min Quantity2Metric Tons
- Price2~3

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail
-
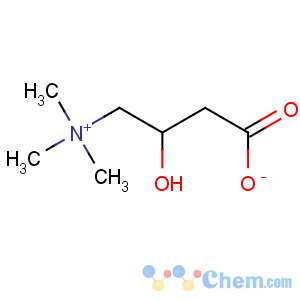 Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure

- L(-)-Carnitine
Detailed Description
hannah at chembj dot com skype: live:hannah_2165Name:
L(-)-Carnitine (Related Reference)
EINECS:
208-768-0
Molecular Formula:
C7H15NO3
CAS Registry Number:
541-15-1
Synonyms:
Vitamin BT; Ammonium, (3-carboxy-2-hydroxypropyl)trimethyl-, hydroxide, inner salt, L- (8CI); (-)-(R)-3-Hydroxy-4-(trimethylammonio)butyrate; (2S)-3-carboxylato-2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylpropan-1-aminium; (S)-carnitine; 1-Propanaminium, 3-carboxy-2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-, inner salt, (2R)-; Ammonium, (3-carboxy-2-hydroxypropyl)trimethyl-, hydroxide,inner salt; Levocarnitine (USP); L-carnitine(VBt); Car-OH; L-Carnitine Base(Usp29); Carnitor (TN); (3S)-3-hydroxy-4-trimethylammonio-butanoate; Carniking 50; (3R)-3-hydroxy-4-trimethylammonio-butanoate; (R)-Carnitine; L-gamma-trimethyl-beta-hydroxybutyrobetaine; 1-Propanaminium,3-carboxy-2-hydroxy-N,N,- N-trimethyl-,inner salt,(2R)-; L-Carnitine EP/USP; L-Carnitine Base (Vitamine BT); L-Carnitine base USP; R-(-)-3-hydroxy-4-trimethylaminobutyrate;
Appearance:
white crystalline powder
Molecular Weight:
161.2
Density:
99%
Melting Point:
208-212℃
Alpha:
-31 o (C=10, H2O)
Storage Temperature:
2-8°C
Refractive index:
-32 ° (C=1, H2O)
Solubility:
2500 g/L (20 °C)
Stability:
Hygroscopic
Usage:
Essential cofactor of fatty acid metabolism; required for the transport of fatty acids through the inner mitochondrial membrane. Synthetized primarily in the liver and kidney; highest concentrations found in heart and skeletal muscle. Dietary source