Procaine powder/ white powder
-
- Product NameProcaine powder/ white powder
- CAS No.59-46-1
- Purity99%
- Min Quantity1.0Kilograms
- Price90.00~15.00

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail
-
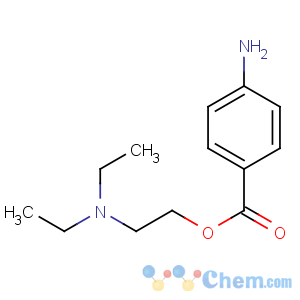 Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Skype:steroidsbioWhatsApp:+8615372437208
Email:steroidsbio@chembj.com
Product Name:Procaine
Alias:Procaine base
CAS NO.:59-46-1
EINECS:200-426-9
Molecular Formula:C13H20N2O2
Molecular Weight:236.3101
Grade:Pharmceutical Grade
Appearance:White Powder
Purity:99%
Usage:Local anesthetic
Procaine is a local anesthetic drug of the amino ester group. It is used primarily to reduce the pain of intramuscular injection of penicillin, and it is also used in dentistry. Owing to the ubiquity of the trade name Novocain, in some regions, procaine is referred to generically as novocaine. It acts mainly as a sodium channel blocker.[1] Today it is used therapeutically in some countries due to its sympatholytic, anti-inflammatory, perfusion-enhancing, and mood-enhancing effects.
Procaine Application
The primary use for procaine is as an anaesthetic.Procaine is used less frequently today since more effective (and hypoallergenic) alternatives such as lidocaine (Xylocaine) exist. Like other local anesthetics (such as mepivacaine, and prilocaine), procaine is a vasodilator, thus is often coadministered with epinephrine for the purpose of vasoconstriction. Vasoconstriction helps to reduce bleeding, increases the duration and quality of anesthesia, prevents the drug from reaching systemic circulation in large amounts, and overall reduces the amount of anesthetic required.[6] Unlike cocaine, a vasoconstrictor, procaine does not have the euphoric and addictive qualities that put it at risk for abuse.
Procaine, an ester anesthetic, is metabolized in the plasma by the enzyme pseudocholinesterase through hydrolysis into para-amino benzoic acid (PABA), which is then excreted by the kidneys into the urine.