Glycerol
-
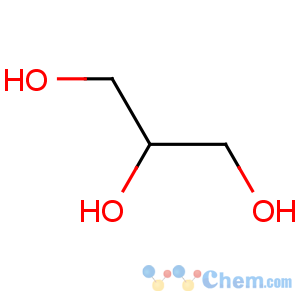
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Glycerol CAS 56-81-5 is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in those lipids known as glycerides.
Glycerol CAS 56-81-5 is a triol with a structure of propane substituted at positions 1, 2 and 3 by hydroxy groups. It has a role as an osmolyte, a solvent, a detergent, a human metabolite, an algal metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite.
Glycerol CAS 56-81-5 is a trihydroxyalcohol with localized osmotic diuretic and laxative effects. Glycerin elevates the blood plasma osmolality thereby extracting water from tissues into interstitial fluid and plasma. This agent also prevents water reabsorption in the proximal tubule in the kidney leading to an increase in water and sodium excretion and a reduction in blood volume. Administered rectally, glycerin exerts a hyperosmotic laxative effect by attracting water into the rectum, thereby relieving constipation. In addition, glycerin is used as a solvent, humectant and vehicle in various pharmaceutical preparations.



