Antipyrine
-
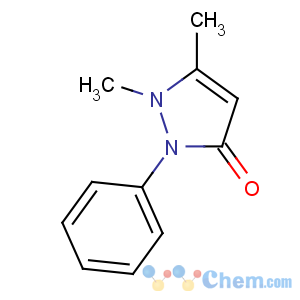
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
1. Quick Detail:
Product Name: Antipyrine
Synonyms: Antipyrene; 2,3-Dimethyl-1-phenyl-3-pyrazolin-5-one; Phenazone; Antipyrine,(2,3-Dimethyl-1-phenyl-3-pyr; antipyrin(R); APYRETINE; Antipyrin; 1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one; 1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-pyrazolidin-3-one; Antypirine; 1,2-dihydro-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-3h-pyrazol-3-one
CAS: 60-80-0
EINECS: 200-486-6
MF: C11H12N2O
MW: 188.23
Assay: 99.2%
Appearance: White powder
Density 1.109g/cm3
Melting point 109-113℃
Boiling point 275°C at 760 mmHg
Refractive index 1.553
Flash point 109.4°C
Water solubility 1000 g/L (20℃)
Vapour Pressur 0.00522mmHg at 25°C
2. Descriptions:
Phenazone (also known as phenazon, antipyrine (USAN), or analgesine) is an analgesic, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and an antipyretic. It was first synthesized by Ludwig Knorr in 1887. Phenazone is synthesized by condensation of phenylhydrazine and ethyl acetoacetate under basic conditions and methylation of the resulting intermediate compound 1-phenyl-3-methylpyrazolone with dimethyl sulfate or methyl iodide. It crystallizes in needles which melt at 156 °C. Potassium permanganate oxidizes it to pyridazine tetracarboxylic acid. Phenazone has an elimination half life of about 12 hours. Indication: Used to relieve pain and fever. Antipyrine is often used in testing the effects of other drugs or diseases on drug-metabolizing enzymes in the liver.

- Antipyrine




