Chlorhexidine Gluconate 5%
-
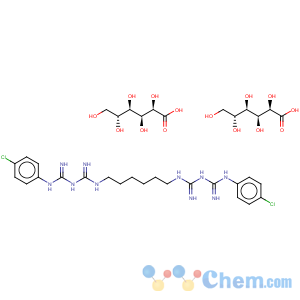
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Chlorhexidine is a diterpene chlorobenzene with a broad antimicrobial activity (Aly and Maibach, 1983; Goldblum et al. 1983; Sebben, 1983). At pH 5.0-8.0, it is most effective against gram-positive (10 mcg/ml) and gram-negative (50 mcg/ml) bacteria. Drug resistance is not an important issue. Unless at a higher temperature, the bacterial spores cannot simply be born, not killed. High serum protein concentration will reduce the antibacterial and bactericidal effects of this product. Blood and other organic substances can slightly reduce its effect (Sheikh, 1986). Although high concentrations of surfactants can reduce the bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects of this product, this problem can be reduced by careful formulation.

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure
