Palmitoylethanolamide(PEA)
-
- Product NamePalmitoylethanolamide(PEA)
- CAS No.544-31-0
- Purity98%
- Min Quantity50Metric Tons
- Price80~150

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail
-
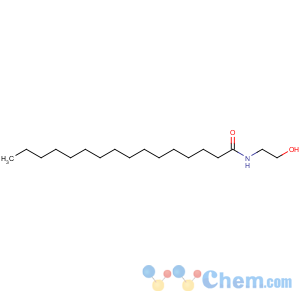 Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure

- Palmitoylethanolamide(PEA)
Detailed Description
Product name: PalmitoylethanolamideOther name: N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)hexadecanamide; PEA; Palmidrol
CAS: 544-31-0
Formula: CHNO
Mol. Mass: 299.49
Appearance: white crystalline powder
Assay: 98%
Packing: 25kg/drum
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) is an endogenous fatty acid amide, belonging to the class of nuclear factor agonists. PEA has been demonstrated to bind to a receptor in the cell-nucleus (a nuclear receptor) and exerts a great variety of biological functions related to chronic pain and inflammation. The main target is thought to be the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α). PEA also has affinity to cannabinoid-like G-coupled receptorsGPR55 and GPR119. PEA cannot strictly be considered a classic endocannabinoid because it lacks affinity for the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2. However, the presence of PEA (and other structurally related N-acylethanolamines) has been known to enhance anandamide activity by a so-called "entourage effect".
Several papers have demonstrated that an imbalance of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) and alterations in the levels of PEA occur in acute and chronic inflammation. For instance during β-amyloid-induced neuroinflammation the deregulation of cannabinoid receptors and its endogenous ligands accompanies the development and progression of disease. PEA has been shown to have anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive, neuroprotective, and anticonvulsant properties.