D-SERINE
-
- Product NameD-SERINE
- CAS No.312-84-5
- Purity99%
- Min Quantity
- Price0~100

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail
-
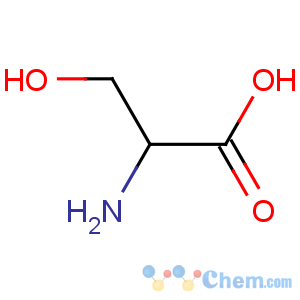 Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure

- D-SERINE
Detailed Description
D-SERINEproduct Name: D-SERINE
Synonyms: D-(+)-Serine; H-D-Ser-OH; D-2-Amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid; D-Ser
Molecular Formula: C3H7NO3
Molecular Weight: 105.09
CAS Registry Number: 312-84-5
EINECS:206-229-4
Packing:25kg/drum
Assay:99%
Basic informations
-----------------------------------------------------
D-Serine is an amino acid found in the brain. Derived from Glycine, d-serine is a neuromodulator, meaning it regulates the activities of neurons.
D-Serine supplementation can reduce symptoms of cognitive decline. It is also able to reduce symptoms of diseases characterized by reduced N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) signaling, which includes cocaine dependence and schizophrenia.
D-Serine’s effect on schizophrenia is well researched, and though it shows promise, it is also unreliable, since d-serine does not always reach the blood after supplementation. Sarcosine may be a more reliable treatment.
D-Serine is a coagonist at NDMA receptors, which means it improves the effects of other compounds that bind with the receptor. These compounds include glutamate and NMDA itself.
D-Serine is often categorized as a Nootropic.
How to Take
--------------------------------------------------------The usual dose used in D-serine studies is 30mg/kg of bodyweight. This correlates to an approximate dosage range of 2,045 - 2,727mg for people between 150 - 200 lbs. This dose appears to be the minimal effective dose for improving cognition in people suffering from a variety of diseases.
Preliminary evidence suggests that doubling or quadrupling the dosage to 60mg/kg and 120mg/kg, respectively, will cause additional benefits for people suffering from schizophrenia.