Contact us
- Company Name: Zhuzhou Yuancheng Hezhong Technology Development Co., Ltd
- Street: No. 388, Huangshan Rd, Tianyuan District, Zhuzhou City, Hunan Province, P.R.China.
- City: zhuzhou
- Province/state: Hunan
- Country/region: China
- Contact Person: Mr.Mao banana
- Department: Sales
- Tel: 86-731-22290202
- Fax: 86-731-22290202
- Email: ychz04@chembj.com

Curcumin
-
- Product NameCurcumin
- CAS No.458-37-7
- Purity≥ 97%
- Min Quantity5000Kilograms
- Price~

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail
-
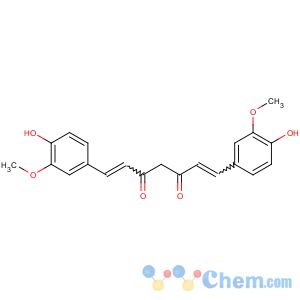 Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure

- Curcumin
Detailed Description
CurcuminMolecular Formula: C21H20O6
Molecular Weight: 368.3799
MS:
CAS: 458-37-7
EINECS: 207-280-5
Solubility: Slightly soluble in hot water
Curcumin is the principal curcuminoids of the popular Indian spice turmeric, which is a member of the ginger family (Zingiberaceae). The other two curcuminoids are desmethoxycurcumin and bis-desmethoxycurcumin. The curcuminoids are polyphenols and are responsible for the yellow color of turmeric. Curcumin can exist in at least two tautomeric forms, keto and enol. The enol form is more energetically stable in the solid phase and in solution.
Curcumin can be used for boron quantification in the so-called curcumin method. It reacts with boric acid forming a red colored compound, known as rosocyanine.
Curcumin is brightly colored and may be used as a food coloring. As a food additive, its E number is E100
Spec.:90%;95% UV
The turmeric which shows on the orange yellow crystallization powder detained from the curcuma by extracting and crystallizating. The major constituent is curcumin.
Characterization: orange yellow powder and have the specific flavor of turmeric.
Color additive in foods, analytical reagent, biological stain, acid base indicator (brownish-red with alkalis, yellow with acids), indicator for boron
Storage: Store in cool & dry place, Keep away from strong light and heat.
Shelf life:24 Months when properly stored.
Appearance: Orange crystalline powder
Function: Several studies have reported that Curcumin is beneficial in lowering LDL and raising HDL or good cholesterol while reducing the lipid peroxidation.Kidney disease may be helped by Curcumin.