Theophylline
-
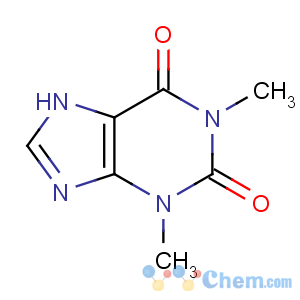
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Product Name: Theophylline
Synonyms: Theophylline anhydrous; 1,3-dimethyl-3,4,5,7-tetrahydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione
CAS: 58-55-9
EINECS: 200-385-7
MF: C7H10N4O2
MW: 182.1799
Assay: 99%
Appearance: White powder
Density 1.62g/cm3
Melting point 270-274℃
Boiling point 390.1°C at 760 mmHg
Refractive index 1.737
Flash point 189.7°C
Water solubility 8.3 g/L (20℃)
Vapour Pressur 2.72E-06mmHg at 25°C
2. Descriptions:
Theophylline, also known as 1,3-dimethylxanthine, is a methylxanthine drug used in therapy for respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma under a variety of brand names. As a member of the xanthine family, it bears structural and pharmacological similarity to theobromine and caffeine.
The main actions of theophylline involve:
relaxing bronchial smooth muscle
increasing heart muscle contractility and efficiency; as a positive inotropic
increasing heart rate: (positive chronotropic)
increasing blood pressure
increasing renal blood flow
anti-inflammatory effects
central nervous system stimulatory effect mainly on the medullary respiratory center.
The main therapeutic uses of theophylline are aimed at:
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
asthma
infant apnea
Blocks the action of adenosine, an inhibitor neurotransmitter that induces sleep, contracts the smooth muscles and relaxes the cardiac muscle.



