Butyl cinnamate
-
- Product NameButyl cinnamate
- CAS No.538-65-8
- Purity99% min
- Min QuantityFCL
- Price~

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail
-
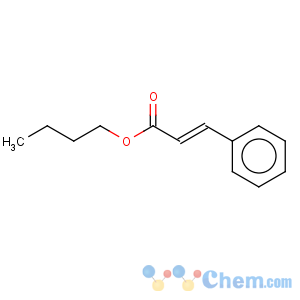 Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
Name: Butyl cinnamateCAS No: 538-65-8
Formula: C13H16O2
Molecular Weight: 204.269
Boiling point: 291.7-313.7?°C(lit.)
Density: 0.9-1.1(g/mL,20/4oC)
Flash point: 153.4-174.2°C
Refractive index?: (20°C)1.5420
Appearance: colorless or light yellow transparent liquid with cinnamon like balsam gas, has a bitter taste.
Solubility: Soluble under normal temperature and pressure, miscible in ethanol, ethyl ether, chloroform and most of the non-volatile oil, a few do not dissolve in water.
Purity:>98%
Package?specification:200kg/blue barrel
Storage: Keep the storage sealed and stored in a cool, dry place, ensuring good ventilation or venting in the workplace. It should be stored separately from oxidants, acids and food chemicals, and should not be mixed. The storage area should be equipped with leakage emergency treatment equipment and suitable containment materials.
Usage:
Butyl cinnamate is naturally present in kumquat. It has sweet fruit and balsamic scent, similar to spicy spices, creamy amber aroma with cocoa beans and fruity notes. The taste is characterized by aroma and fruity aroma, similar to the sweet taste of red currant. It is often used as a blending agent and modifier for rock rose products and amber-dragon fragrant flavors in fragrance formulations. It can also be well coordinated with oakmoss and sapwood products, patchouli oil, veterinary oil, coumarin, jasmine aldehyde, and nitro musk. Also commonly used in the formulation of oriental fragrance. It can also be used in food flavors such as chocolate, cherry, cocoa, peach, strawberry, and raspberry.
Butyl cinnamate is used in perfumes, synthetic indigo, and certain drugs. One major use is in the perfume industry for the manufacture of methyl, ethyl, and benzyl esters.Cinnamic acid is a precursor of the sweetener aspartame, which is enzymatically aminated to phenylalanine. Butyl cinnamate is also a self-inhibiting factor produced by fungal spores to inhibit germination.