Cinnamic acid
-
- Product NameCinnamic acid
- CAS No.140-10-3
- Purity
- Min Quantity
- Price~

 View Contact Detail
View Contact Detail
-
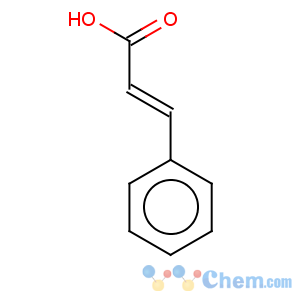 Molecular Structure
Molecular Structure
Detailed Description
CAS#: 140-10-3Appearance: white to light yellow crystal powder
Fragrance: unique scent
Structure: C9H8O2
Formula weight: 148.16
Assay: ??9%
Melting point: 132.5-134.5 centigrade
Heavy metals (ppm) : ??0ppm
Residue on ignition: ??.1%
Packing: 25kg/plastic bag
Usage: In biological chemistry, cinnamic acid is a key intermediate in shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways. Shikimic acid is a precursor of many alkaloids, aromatic amino acids, and indole derivatives. Phenylpropanoid are a class of plant metabolites based on phenylalanine. They are widely distributed in plants fulfilling many functions including plant defense mechanism, pigmentation and external signaling system. Phenylalanine is first converted to cinnamates, coumarines, caffeic acids, ferulic acids, and sinapic acids. Cinnamic acid is the precursor of these acids. Cinnamic acid is the parent compound of its esters which are more volatile to be transported to other parts easily.