Title: Heparin
CAS Registry Number: 9005-49-6
Synonyms: Heparinic acid
Trademarks: Arteven (Boehringer, Ing. Italia); Leparan (Italfarmaco)
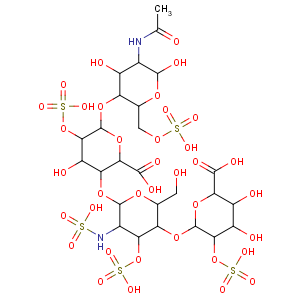
Literature References: Glycosaminoglycan with anticoagulant activity. Heterogenous mixture of variably sulfated polysaccharide chains composed of repeating units of D-glucosamine and either L-iduronic or D-glucuronic acids. Mol wt ranges from 6000-30000 Da. Biosynthesized and stored in mast cells of various animal tissues, particularly liver, lung or gut. Commercial heparin is isolated from beef lung or pork intestinal mucosa. Isoln from mammalian tissue: Howell,
Am. J. Physiol. 63, 434 (1922-23);
71, 553 (1924-25); Korn,
J. Biol. Chem. 234, 1325 (1959); L. B. Jaques,
Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37, 1183 (1959); J. A. Bush
et al., US 2884358 (1959 to So. Calif. Gland). Purification: G. Nominé
et al., US 2989438 (1961 to UCLAF); Toccaceli,
US 3016331 (1962 to Ormonoterapia Richter); L. Roden
et al., Methods Enzymol. 26, 73 (1972). Structural studies: M. L. Wolfrom,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 72, 5796 (1950); Velluz
et al., Compt. Rend. 247, 1521 (1958); M. L. Wolfrom
et al., J. Org. Chem. 29, 540 (1964). Configuration of glycosidic linkages: M. L. Wolfrom
et al., ibid. 31, 1173 (1966); A. S. Perlin
et al., Can. J. Chem. 48, 2260 (1970); T. Helting, U. Lindahl,
J. Biol. Chem. 246, 5442 (1971). Identification of L-iduronic acid residues: A. S. Perlin
et al., Carbohydr. Res. 7, 369 (1968). Antithrombotic activity results from the binding and activation of
antithrombin III, a plasma protein which inhibits several enzymes in the coagulation cascade: R. D. Rosenberg,
Fed. Proc. 36, 10 (1977). Anticoagulant activity is related to the mol wt of the polysaccharide fragments; low molecular weight components exhibit decreased hemorrhagic effects while retaining antithrombin binding ability: L.-O. Andersson
et al., Thromb. Res. 15, 531 (1979); T. W. Barrowcliffe
et al., Br. J. Haematol. 41, 573 (1979); J. Hirsch
et al., Semin. Thromb. Hemostasis 11, 13 (1985). Characterization of the antithrombin binding site: U. Lindahl
et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 3198 (1979); J. Choay
et al., Thromb. Res. 18, 573 (1980). Synthesis of the pentasaccharide corresponding to the binding site sequence:
eidem, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 116, 492 (1983). Symposium on structure, activity and clinical applications:
Fed. Proc. 36, 9-116 (1977). Review of mechanism of action: I. Bj?rk, U. Lindahl,
Mol. Cell. Biochem. 48, 161-182 (1982); of structure-activity relationships and prepn of low mol wt fractions: B. Casu,
Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 43, 51-134 (1985); of biosynthesis: U. Lindahl
et al., Trends Biochem. Sci. 11, 221-225 (1986). Comprehensive description: F. Nachtmann
et al., Anal. Profiles Drug Subs. 12, 215-276 (1983). Overview of clinical results in pulmonary embolism and venous thrombosis: R. Collins
et al., N. Engl. J. Med. 318, 1162-1170 (1988); J. Hirsh,
ibid. 324, 1565-1574 (1991); of clinical studies with low mol wt heparinoids: H. ten Cate
et al., Am. J. Hematol. 27, 146-153 (1988).
Properties: Heparin has a rotation of [a]D20 +55°.
Optical Rotation: [a]D20 +55°
Derivative Type: Calcium salt
CAS Registry Number: 37270-89-6
Trademarks: Calciparine (Sanofi Winthrop); Ecasolv (Lepetit)
Derivative Type: Magnesium salt
CAS Registry Number: 54479-70-8
Synonyms: Magnesium heparinate
Trademarks: Cutheparine (Biosedra)
Properties: Sol in water. Insol in organic solvents.
Derivative Type: Potassium salt
CAS Registry Number: 9005-48-5
Trademarks: Clarin (formerly) (Pfizer)
Derivative Type: Sodium salt
CAS Registry Number: 9041-08-1
Synonyms: Heparin sodium
Trademarks: Hepsal (Weddel); Lipo-Hepin (3M Pharma); Liquémin (Roche); Longheparin; Monoparin (CP Pharm.); Panheprin (Abbott); Pularin; Liquaemin Sodium (Organon); Minihep (Leo Pharm); Thromboliquine; Thrombophob (Nordmark); Unihep (Leo Pharm)
Properties: White to grayish-brown amorphous powder. Odorless, hygroscopic. [a]D25 +47° (c = 1.5 in water). One gram dissolves in 20 ml water. Sol in saline soln. Practically insol in alcohol, acetone, benzene, chloroform, ether. pH of 1% aq soln = 6.0 to 7.5. Absorption spectrum: Burson
et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 78, 5874 (1956). Ampuled solns may be stored at room temp for at least 12 months. Commercially available ampuled, sterile solns contain 0.5% phenol or chlorobutanol as preservative.
Optical Rotation: [a]D25 +47° (c = 1.5 in water)
Therap-Cat: Anticoagulant.
Therap-Cat-Vet: Anticoagulant.
Keywords: Anticoagulant.