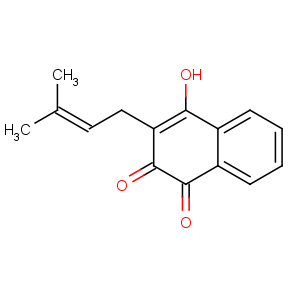
Title: Lapachol
CAS Registry Number: 84-79-7
CAS Name: 2-Hydroxy-3-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-1,4-naphthalenedione
Synonyms: lapachic acid; taiguic acid; tecomin; greenhartin
Manufacturers' Codes: NSC-11905
Molecular Formula: C15H14O3
Molecular Weight: 242.27
Percent Composition: C 74.36%, H 5.82%, O 19.81%
Literature References: Yellow crystalline material derived from the heartwood of Asian and South American bignoniaceous plants, esp Surinam greenheart, Taigu wood, Lapacho heartwood and Bethabarra wood: Arnoudon,
Compt. Rend. 41, 1152 (1857); Stein,
J. Prakt. Chem. 99, 1 (1866); Paterno,
Gazz. Chim. Ital. 9, 506 (1879); Greene, Hooker,
Am. Chem. J. 11, 267 (1889). Structure: Paterno,
Gazz. Chim. Ital. 12, 337 (1882); Hooker
J. Chem. Soc. 61, 611 (1892);
69, 1355 (1896);
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 58, 1168 (1936). Synthesis: Fieser,
ibid. 49, 857 (1927); Hooker,
ibid. 58, 1181 (1936); G. R. Pettit, L. E. Houghton,
J. Chem. Soc. C 1971, 509. Although it is related structurally to vitamin K,
q.v., it does not possess antihemorrhagic activity: H. J. Almquist, A. A. Klose,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 61, 1923 (1939); L. F. Fieser
et al., J. Biol. Chem. 137, 659 (1941). It is reported to be an inhibitor of respiratory processes: E. G. Ball
et al., ibid. 168, 257 (1947). Lapachol has also exhibited antitumor activity vs Walker 256 carcinoma: K. V. Rao
et al., Proc. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 8, 55 (1967). Mass spectrometry: T. A. Elwood
et al., Org. Mass Spectrom. 3, 841 (1970). Chromatographic detection: M. H. Simatupang
et al., J. Chromatogr. 52, 180 (1970). Pharmacology: S. M. Sieber
et al., Cancer Treat. Rep. 60, 1127 (1976). Toxicity study: R. K. Morrison
et al., Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 17, 1 (1970). Review of antitumor activity: K. V. Rao,
Cancer Chemother. Rep. Part 2 4 (4), 11-17 (1974).
Properties: Yellow prisms from alcohol or ether, mp 140°. uv max: 251.5, 278, 331 nm (log e 4.38, 4.28, 3.43). Soluble in alcohol, chloroform, benzene, acetic acid, slightly sol in ether, hot water. Sol in aq NaOH solns forming a bright red sodium salt. LD50 in male, female BALB/c mice (g/kg): 0.487; 0.792 orally (Morrison).
Melting point: mp 140°
Absorption maximum: uv max: 251.5, 278, 331 nm (log e 4.38, 4.28, 3.43)
Toxicity data: LD50 in male, female BALB/c mice (g/kg): 0.487; 0.792 orally (Morrison)