Title: Eucalyptus
Literature References: Genus of evergreen trees of the Family
Myrtaceae, having aromatic blue-grey leaves that yield a characteristic essential oil.
Habit. Australia, cultivated in subtropical regions of Europe, Africa, Asia and U.S. More than 700 species are known; the Australian blue-gum,
Eucalyptus globulus Labill., is the most predominant and said to be richest in essential oil.
Constit. 0.5-3.5% volatile oil, resins, tannins, polyphenolic acids, and flavonoids such as quercetin, rutin, eucalyptin. Review of botany, cultivation and uses: M. Forrest,
Biologist 47, 139-142 (2000); of pharmacology and medicinal uses: A. Y. Leung, S. Foster,
Encyclopedia of Common Natural Ingredients, (Wiley-Interscience, Hoboken, 2nd Ed., 2003) pp 232-234; J. Gruenwald
et al., PDR for Herbal Medicines (Medical Economics, Montvale, 3rd Ed., 2004) pp 293-297.
Derivative Type: Volatile oil
CAS Registry Number: 8000-48-4
Synonyms: Oil of eucalyptus
Literature References: Obtained by steam distillation from fresh leaves of
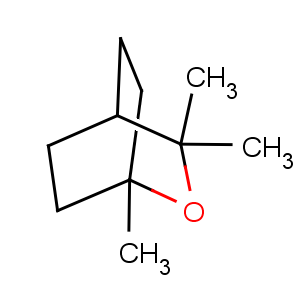
E. globulus. Constit. 70-80% Eucalyptol (1,8-cineole), a-pinene,
d-limonene,
p-cymene, a-phellandrene, 1-a-terpineol. Description: E. Guenther,
The Essential Oils vol. 4 (van Nostrand, New York, 1950) pp 437-525.
Properties: Colorless to pale yellow liquid; characteristic camphoraceous odor; pungent, spicy, cooling taste. d2525 0.905-0.925.
nD20 1.458-1.470. Almost insol in water; sol in 5 vols 70% alcohol.
Keep well closed, cool and protected from light.
Index of refraction: nD20 1.458-1.470
Density: d2525 0.905-0.925
Use: Wood for timber, pulp, fuel, charcoal; cut foliage in floral arrangements. Oil as fragrance component in soaps, creams, lotions and as flavoring agent in pharmaceuticals, toothpastes, mouthwashes.
Therap-Cat: Oil as expectorant, antiseptic, externally for rheumatism.