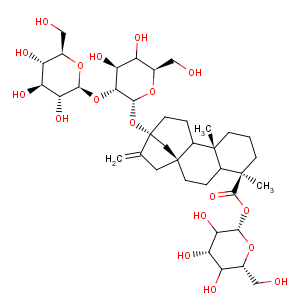
Title: Stevioside
CAS Registry Number: 57817-89-7
CAS Name: (4a)-13-[(2-
O-b-D-Glucopyranosyl-b-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]kaur-16-en-18-oic acid b-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Synonyms: steviosin
Molecular Formula: C38H60O18
Molecular Weight: 804.87
Percent Composition: C 56.71%, H 7.51%, O 35.78%
Literature References: Isolated from leaves of
Stevia rebaudiana (Bert.) Hemsl. (
Eupatorium rebaudianum Bert.),
Compositae, also called
yerba dulce. Habit. Paraguay. Isoln and structure: Wood
et al., J. Org. Chem. 20, 875 (1955). Review of botany: Samaniego,
Rev. Farm. (Buenos Aires) 88, 199 (1946). Review of chemistry and use as sweetening agent: Bell,
Chem. Ind. (London) 1954, 897; Fletcher, Jr.,
Chemurg. Dig. 14, 7, 18 (July-Aug. 1955);
Chem. Eng. News 34, 124 (1956). Total synthesis:
eidem, Tetrahedron 36, 2641 (1980). Synthesis and sensory evaluation of analogs: G. E. Dubois
et al., J. Med. Chem. 24, 1269 (1981).
Properties: Hygroscopic crystals, mp 198°. [a]D25 -39.3° (c = 5.7 in H2O). 300 times as sweet as cane sugar. One gram dissolves in 800 ml water. Sol in dioxane. Slightly sol in alc.
Melting point: mp 198°
Optical Rotation: [a]D25 -39.3° (c = 5.7 in H2O)
Derivative Type: Steviol
CAS Registry Number: 471-80-7
CAS Name: (4a)-13-Hydroxykaur-16-en-18-oic acid
Synonyms: hydroxydehydrostevic acid
Literature References: Aglucon of stevioside, the sweet glucoside abundant in leaves and stems of
Stevia rebaudiana Bert. Absolute configuration: Mosettig
et al., ibid. 85, 2305 (1963). Biosynthesis: Ruddat
et al., Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 110, 496 (1965). Total synthesis of
dl-form: Mori
et al., Tetrahedron Lett. 1970, 2411; Cook, Knox,
ibid. 4091;
eidem, Tetrahedron 28, 3217 (1972).
Properties: Needles from methanol or ethanol + water, mp 215°. [a]D -94.7°.
Melting point: mp 215°
Optical Rotation: [a]D -94.7°
Use: Has been proposed as non-nutritive sweetening agent.