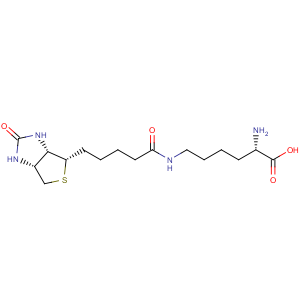
Title: Biocytin
CAS Registry Number: 576-19-2
CAS Name: N6-[5-(Hexahydro-2-oxo-1
H-thieno[3,4-
d]imidazol-4-yl)-1-oxopentyl]-L-lysine
Synonyms: e-
N-biotinyl-L-lysine; biotin complex of yeast
Molecular Formula: C16H28N4O4S
Molecular Weight: 372.48
Percent Composition: C 51.59%, H 7.58%, N 15.04%, O 17.18%, S 8.61%
Literature References: A naturally occurring complex of biotin. Contains 65.6% biotin. Isoln: Wright
et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 72, 1048 (1950);
74, 1996 (1952). Structure: Peck
et al., ibid. 72, 1048 (1950);
74, 1999 (1952). Synthesis: Wolf
et al., ibid. 74, 2002 (1952); Weijlard
et al., ibid. 76, 2505 (1954); Wolf, Folkers,
US 2710298 (1955 to Merck & Co.). Purification: McCormick, F?ry,
Methods Enzymol. 18 (pt A), 413 (1970).
Review: A. F. Wagner, K. Folkers,
Vitamins and Coenzymes (Wiley, New York, 1964) pp 138-159.
Properties: Crystals, mp 241-243°. Upon rapid crystn from dil methanol or dil acetone, mp 228-230° (dec); upon slow crystn sinters at 227°. mp 245-252° (dec, microblock). Crystals from water, mp 228.5°. [a]D25 +53° (c = 1.05 in 0.1
N NaOH). Infrared absorption spectrum:
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 74, 2001 (1952). Freely sol in water, glacial acetic acid. Less sol in alc. Practically insol in acetone and most other organic solvents. When subjected to strong acid hydrolysis (at least 3
N at 120° for one hour) biocytin yields biotin and L-lysine. Forms a crystalline hydrochloride. Biocytin is characterized microbiologically by its availability as a source of biotin to
Lactobacillus casei, L. delbrückii LD 5,
L. acidophilus, Streptococcus fecalis R,
Neurospora crassa, and
Saccharomyces carlsbergensis and by its unavailability as a source of biotin to
Lactobacillus arabinosus, L. pentosus, and
Leuconostoc mesenteroides P-60.
Melting point: mp 241-243°; mp 228-230° (dec); mp 245-252° (dec, microblock); mp 228.5°
Optical Rotation: [a]D25 +53° (c = 1.05 in 0.1
N NaOH)