References of 3H-2-Benzopyran-7-carboxylicacid, 4,6-dihydro-8-hydroxy-3,4,5-trimethyl-6-oxo-, (3R,4S)-
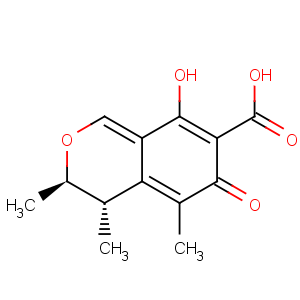
Title: Citrinin
CAS Registry Number: 518-75-2
CAS Name: (3
R,4
S)-4,6-Dihydro-8-hydroxy-3,4,5-trimethyl-6-oxo-3
H-2-benzopyran-7-carboxylic acid
Trademarks: Antimycin
Molecular Formula: C13H14O5
Molecular Weight: 250.25
Percent Composition: C 62.39%, H 5.64%, O 31.97%
Literature References: Antibiotic substance produced by a white spore aspergillus which has been placed under the species name
Aspergillus niveus (Thorn and Raper). Also produced in small quantities by
Penicillium citrinum: Hetherington, Raistrick,
Trans. R. Soc. London B220, 269 (1931); Raistrick, Smith,
Chem. Ind. (London) 60, 828 (1941); Timonin,
Science 96, 494 (1942); Timonin, Rovatt,
Can. J. Public Health 35, 80 (1944). Identity with antimycin: Haese,
Arch. Pharm. 296, 227 (1963). Structure: Brown
et al., J. Chem. Soc. 1949, 867; Warren
et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79, 3812 (1957); Kovac
et al., Nature 190, 1104 (1961). Synthesis: Cartwright
et al., J. Chem. Soc. 1949, 1563; J. A. Barber
et al., J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1986, 2101. Stereochemistry: Cram,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 72, 1001 (1950); Mehta, Whalley,
J. Chem. Soc. 1963, 3777; Mathieson, Whalley,
ibid. 1964, 4640. Physical characteristics and toxicity: Nagai
et al., Chem. Zentralbl. 1958, 8088,
C.A. 55, 1914 (1961). Crystal and molecular structure: Rodig,
Chem. Commun. 1971, 1553. Biosynthesis: J. Barber
et al., J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1981, 2577; L. Colombo
et al., ibid. 2594. Physicochemical data: A. E. Pohland
et al., Pure Appl. Chem. 54, 2219 (1982). Toxicology: A. M. Ambrose, F. De Eds,
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 88, 173 (1946).
Review: Saito
et al., "Yellowed Rice Toxins" in
Microbial Toxins vol. VI, A. Ciegler, S. Kadis, A. Ajl, Eds. (Academic Press, New York, 1971) pp 357-367.
Properties: Lemon-yellow needles from alcohol, dec 175°. [a]D18 -37.4° (c = 1.15 in alc.). uv max: 250, 331 nm (E1%1cm 370, 418). Strong acid. Practically insol in water. Sol in alcohol, dioxane, dilute alkali. Solns change color with changes in pH, from lemon-yellow at pH 4.6 to cherry-red at pH 9.9.
Poisonous! LD50 in mice, rats (mg/kg): 35, 67 i.p. (Ambrose, De Eds).
Optical Rotation: [a]D18 -37.4° (c = 1.15 in alc.)
Absorption maximum: uv max: 250, 331 nm (E1%1cm 370, 418)
Toxicity data: LD50 in mice, rats (mg/kg): 35, 67 i.p. (Ambrose, De Eds)
Derivative Type: Methyl citrinin
Molecular Formula: C14H16O5
Molecular Weight: 264.27
Percent Composition: C 63.63%, H 6.10%, O 30.27%
Properties: Plates from benzene, dec 139°. [a]D18 +217.1° (c = 0.38 in acetone). uv max: 260, 334 nm (E1%1cm 520, 151.6). Sol in hot alcohol; moderately sol in chloroform. Practically insol in petr ether.
Optical Rotation: [a]D18 +217.1° (c = 0.38 in acetone)
Absorption maximum: uv max: 260, 334 nm (E1%1cm 520, 151.6)
Derivative Type: Dihydrocitrinin
Molecular Formula: C13H16O5
Molecular Weight: 252.26
Percent Composition: C 61.90%, H 6.39%, O 31.71%
Properties: Prisms from benzene, dec 171°. [a]D18 -18.8° (c = 4.148 in chloroform). uv max: 260, 330 nm (E1%1cm 400, 100). Sol in alcohol, acetone, chloroform; sparingly sol in benzene, petr ether.
Optical Rotation: [a]D18 -18.8° (c = 4.148 in chloroform)
Absorption maximum: uv max: 260, 330 nm (E1%1cm 400, 100)