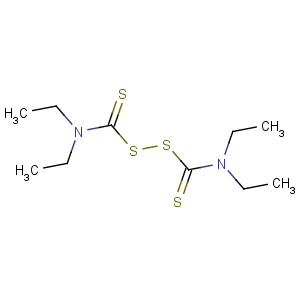
Title: Disulfiram
CAS Registry Number: 97-77-8
CAS Name: Tetraethylthioperoxydicarbonic diamide
Synonyms: bis(diethylthiocarbamoyl) disulfide; tetraethylthiuram disulfide; bis(diethylthiocarbamyl) disulfide; teturamin; TTD
Trademarks: Antabuse (Odyssey); Esperal (Sanofi-Synthelabo); Etabus (Ferring)
Molecular Formula: C10H20N2S4
Molecular Weight: 296.54
Percent Composition: C 40.50%, H 6.80%, N 9.45%, S 43.25%
Literature References: Prepn: Bailey,
US 1796977 (1931 to Roessler and Hasslacher); Adams, Newser,
US 1782111 (1931 to Naugatuck);
cf. Cummings, Simmons,
Ind. Eng. Chem. 20, 1173 (1928). Toxicity study: Child, Cramp,
Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 8, 305 (1952). Comprehensive description: N. G. Nash, R. D. Daley,
Anal. Profiles Drug Subs. 4, 168-191 (1975).
Properties: Crystals, mp 70°. d 1.30. Practically insol in water (0.02 g/100 ml). Sol in alcohol (3.82 g/100 ml), in ether (7.14 g/100 ml), also sol in acetone, benzene, chloroform, carbon disulfide. LD50 orally in rats: 8.6 g/kg (Child, Cramp).
Melting point: mp 70°
Density: d 1.30
Toxicity data: LD50 orally in rats: 8.6 g/kg (Child, Cramp)
CAUTION: Potential symptoms of overexposure are irritation of eyes, skin, respiratory system; sensitization dermatitis; lassitude, fatigue, tremor, restlessness, headache, dizziness; metallic taste, peripheral neuropathy; liver damage. Ingestion of alcohol after disulfiram administration causes intense vasodilation and flushing of face and neck, restlessness, anxiety; tachycardia and tachypnea; headache, nausea, vomiting, hyperpnea, chest pains, sweating, pallor, hypotension.
See NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards (DHHS/NIOSH 97-140, 1997) p 122;
Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products, R. E. Gosselin
et al., Eds. (Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 5th ed., 1984) Section III, pp 159-163, 383-386.
Use: Rubber accelerator; vulcanizer; seed disinfectant; fungicide.
Therap-Cat: Alcohol deterrent.
Keywords: Alcohol Dependence Treatment.