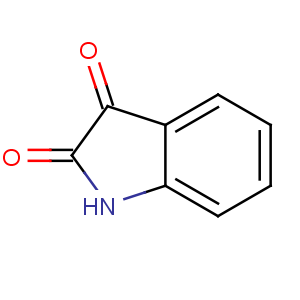
Title: Isatin
CAS Registry Number: 91-56-5
CAS Name: Indole-2,3-dione
Synonyms: 2,3-indolinedione; 2,3-diketoindoline
Molecular Formula: C8H5NO2
Molecular Weight: 147.13
Percent Composition: C 65.31%, H 3.43%, N 9.52%, O 21.75%
Literature References: May be obtained by oxidation of indigo or of oxygenated indoles such as indoxyl, oxindole, or dioxindole: Erdmann,
J. Prakt. Chem. [1]
24, 1 (1841); Laurent,
ibid. 25, 430 (1842);
DE 229815 in
Frdl. 10, 353 (1910);
JP 152932 (1942 to ICI);
C.A. 44, 1544d (1950). Synthesis: Sandmeyer,
Helv. Chim. Acta 2, 234 (1919);
GB 128122 in
C.A. 13, 2375 (1919); Marvel, Hiers,
Org. Synth. coll. vol. I (2nd ed., 1941) p 327; Wibaut, Gerling,
Rec. Trav. Chim. 50, 41 (1931); Neunhoeffer, Lehmann,
Ber. 94, 2960 (1961); Ziegler
et al., Monatsh. Chem. 94, 453 (1963). May be isolated from the urine of rabbits that are fed
o-nitrophenylglyoxylic acid: Bohm,
Z. Physiol. Chem. 265, 210 (1940). Pharmacology: Singh,
Indian Vet. J. 48, 672 (1971).
Reviews: Heller,
Ueber Isatin, Isatyd, Dioxindol und Indophenin (F. Enke, Stuttgart, 1931); Sumpter,
Chem. Rev. 34, 393 (1944). Discussion of chemistry of isatin: Morton,
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds (New York, 1946) pp 126-132.
Properties: Orange-colored monoclinic prisms. mp 203.5° (partial sublimation). Absorption spectrum: Hartley, Dobbie,
J. Chem. Soc. 75, 647, 656. Freely sol in boiling alcohol; sol in ether and in boiling water with reddish-brown color; sol in alkali hydroxide solns with a violet color becoming yellow on standing. The alc soln imparts a persistent, disagreeable odor to the human skin. Extremely weak base, forms a crystalline perchlorate, C8H5NO2.HClO4.2H2O.
Melting point: mp 203.5° (partial sublimation)
Use: Manuf vat dyes. In analytical chemistry as a reagent for cuprous ions, mercaptans, thiophene, and indican.