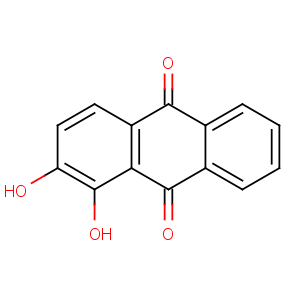
Title: Alizarin
CAS Registry Number: 72-48-0
CAS Name: 1,2-Dihydroxy-9,10-anthracenedione
Synonyms: 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone; C.I. Mordant Red 11; C.I. Pigment Red 83; C.I. 58000
Molecular Formula: C14H8O4
Molecular Weight: 240.21
Percent Composition: C 70.00%, H 3.36%, O 26.64%
Literature References: Occurs in the root of the madder plant (
Rubia tinctorum L.,
Rubiaceae; Krappwurzel) in combination with 2 mols glucose, called ruberythric acid. Was known and used in ancient Egypt, Persia, and India. Synthesized from 2-anthraquinonesulfonic acid sodium salt : Caro
et al., Ber. 3, 359 (1870); Perkin,
Ber. 9, 281 (1876). Historical
review: Fieser,
J. Chem. Educ. 7, 2609 (1930). Laboratory prepn: Gattermann-Wieland,
Laboratory Methods of Organic Chemistry (New York, 1937). Modern methods of manufacture: Pohl,
Ullmanns Encyklop?die der technischen Chemie vol. I, p 200; Fierz-David and Blangey,
Grundlegende Operationen der Farbenchemie (Vienna, 5th ed., 1943).
See also Colour Index vol. 4, (3rd ed., 1971) p 4513.
Properties: Orthorhombic, orange needles by sublimation or from abs alc. Solvated scales from dil alc or by evaporation from ether. Sublimes at 110° (2 mm Hg). mp 290°. bp 430°. Absorption spectrum: Moir,
J. Chem. Soc. 1927, 1810. Soly in water at 18°: 2.1′10-6 mols/l; at 25°: 2.5′10-6 mols/l. Sol in 300 parts boiling water; moderately sol in alcohol, freely in hot methanol and in ether at 25°. Also sol in benzene, toluene, xylene, pyridine, carbon disulfide, glacial acetic acid. Sol in water solns of alkalies with blue color, but without fluorescence. Fluorescent solns indicate unchanged 2-anthraquinone sodium sulfonate.
Melting point: mp 290°
Boiling point: bp 430°
Derivative Type: 1-Methyl ether
Molecular Formula: C15H10O4
Molecular Weight: 254.24
Percent Composition: C 70.86%, H 3.96%, O 25.17%
Properties: Orange needles with 1H2O from dil methanol. When dried at 100° mp 179°.
Melting point: mp 179°
Derivative Type: 2-Methyl ether
Molecular Formula: C15H10O4
Molecular Weight: 254.24
Percent Composition: C 70.86%, H 3.96%, O 25.17%
Properties: Orange needles from alcohol, mp 231°.
Melting point: mp 231°
Derivative Type: Dimethyl ether
Molecular Formula: C16H12O4
Molecular Weight: 268.26
Percent Composition: C 71.64%, H 4.51%, O 23.86%
Properties: Golden-yellow needles from alcohol, mp 215°.
Melting point: mp 215°
Use: In the manufacture of acid and chrome dyes for wool; acid-base indicator (in 0.5% alcoholic soln; pH: yellow 5.5, red 6.8); in spot tests as reagent for aluminum, indium, mercury, zinc, and zirconium; biological stain.