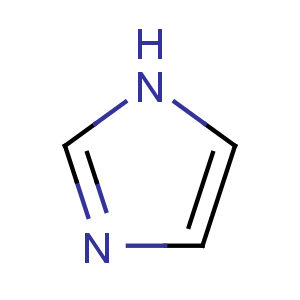
Title: Imidazole
CAS Registry Number: 288-32-4
Synonyms: Glyoxaline; 1,3-diazole; iminazole; miazole; pyrro[
b]monazole; 1,3-diaza-2,4-cyclopentadiene
Molecular Formula: C3H4N2
Molecular Weight: 68.08
Percent Composition: C 52.93%, H 5.92%, N 41.15%
Literature References: Prepd by the action of ammonia on glyoxal: Debus,
Ann. 107, 204 (1858); from glyoxal, ammonia, and formaldehyde: Radziszewski,
Ber. 15, 1493 (1882); Behrend, Schmitz,
Ann. 277, 338 (1893); vapor phase synthesis from formamide and ethylenediamine in presence of a dehydrogenation catalyst: Green,
US 3255200 (1966 to Air Products and Chemicals). Crystal structure: B. M. Craven
et al., Acta Crystallogr. 33B, 2585 (1977). Acute toxicity: Nishie
et al., Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 14, 301 (1969).
Review: Pyman,
J. Soc. Dyers Colour. 36, 107 (1920).
Monograph: K. Hofmann,
Imidazole and Its Derivatives (Interscience, New York, 1953). Review of imidazole chemistry: Grimmett,
Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 12, 103-183 (1970).
Properties: Stout prisms from benzene. mp 90-91°. bp760 257°; bp20 165-168°; bp12 138.2°. Weak base. pK (25°): 6.92. Absorption spectrum: Rosanov,
J. Russ. Phys. Chem. Soc. 48, 1241 (1916);
Chem. Zentralbl. 1923, III, 1080. Freely sol in water, alcohol, ether, chloroform, pyridine; slightly sol in benzene; very sparingly sol in petr ether. LD50 in mice (mg/kg): 610 i.p.; 1880 orally (Nishie).
Melting point: mp 90-91°
Boiling point: bp760 257°; bp20 165-168°; bp12 138.2°
pKa: pK (25°): 6.92
Toxicity data: LD50 in mice (mg/kg): 610 i.p.; 1880 orally (Nishie)