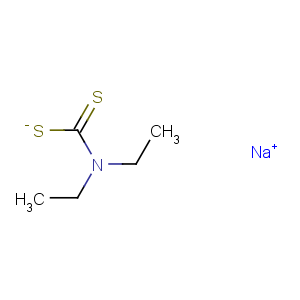
Title: Ditiocarb Sodium
CAS Registry Number: 148-18-5
CAS Name: Diethylcarbamodithioic acid sodium salt
Synonyms: diethyldithiocarbamic acid sodium salt; diethyldithiocarbamate sodium; dithiocarb; DTC; DDC; DEDC; DDTC; DeDTC
Trademarks: Imuthiol
Molecular Formula: C5H10NNaS2
Molecular Weight: 171.26
Percent Composition: C 35.07%, H 5.89%, N 8.18%, Na 13.42%, S 37.45%
Line Formula: (C2H5)2NCS2Na
Literature References: Chelating agent with strong affinity for Hg, Cu, Ni and Zn. Also active as T-cell specific immunostimulant. Prepn: A. M. Clifford, J. G. Lichty,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 54, 1163 (1932); A. L. Klebanskii, L. P. Fomina,
Zh. Obshch. Khim. 30, 794 (1960). Absorption spectrum: H. P. Koch,
J. Chem. Soc. 1949, 401. Inhibition of superoxide dismutase in mice: R. E. Heikkila
et al., J. Biol. Chem. 251, 2182 (1976); of cisplatin nephrotoxicity in rats: R. F. Borch
et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 5441 (1980). Clinical use in acute nickel carbonyl poisoning: F. W. Sunderman, F. W. Sunderman Jr.,
Am. J. Med. Sci. 236, 26 (1958); F. W. Sunderman,
Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 9, 1 (1979); in acute cadmium poisoning: G. R. Gale
et al., ibid. 11, 476 (1981) and
13, 207 (1983). Specific effects on T-cell regulation: A. Pompidou
et al., Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 7, 561 (1985). Clinical evaluation in T-cell deficient diseases: E. Lemarie
et al., Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 8, 51 (1986); in AIDS-related complex: A. Pompidou
et al., Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 9, 263 (1986). Review of pharmacology, toxicity and clinical uses: G. Renoux,
J. Pharmacol. 13, Suppl. 1, 95-134 (1982); of immunopharmacology and use in cancer immunotherapy: G. Renoux
et al., Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 166, 223-239 (1983).
Derivative Type: Trihydrate
Molecular Formula: C5H10NNaS2.3H2O
Molecular Weight: 225.31
Percent Composition: C 26.65%, H 7.16%, N 6.22%, Na 10.20%, S 28.46%, O 21.30%
Properties: Thin, irregular plate-like crystals from acetone, mp 94-102°. Also reported as 90-92° (Sunderman, Sunderman). Freely sol in water; sol in ethanol, methanol, acetone. Insol in ether, benzene. The aq soln is alkaline to litmus and phenolphthalein and slowly dec. (pH of 10% aq soln is 11.6 at room temp). The addition of an acid to the aq soln produces a white turbidity due to the liberation of carbon disulfide. uv max (ethanol): 257, 290 nm (e 1200, 13000). LD50 orally in rats, mice: 2830, 1870 mg/kg; i.v. in mice: >1000 mg/kg (Renoux, 1982).
Melting point: mp 94-102°
Absorption maximum: uv max (ethanol): 257, 290 nm (e 1200, 13000)
Toxicity data: LD50 orally in rats, mice: 2830, 1870 mg/kg; i.v. in mice: >1000 mg/kg (Renoux, 1982)
Use: For colorimetric determination of small quantities of copper and for its separation from other metals.
Therap-Cat: Immunomodulator. Chelating agent (copper); Wilson's Disease treatment. Antidote (nickel, cadmium poisoning).
Keywords: Antidote (Heavy Metal Poisoning); Chelating Agent; Immunomodulator; Wilson's Disease Treatment.